What is Vulva Cancer?
What is Vulva Cancer?
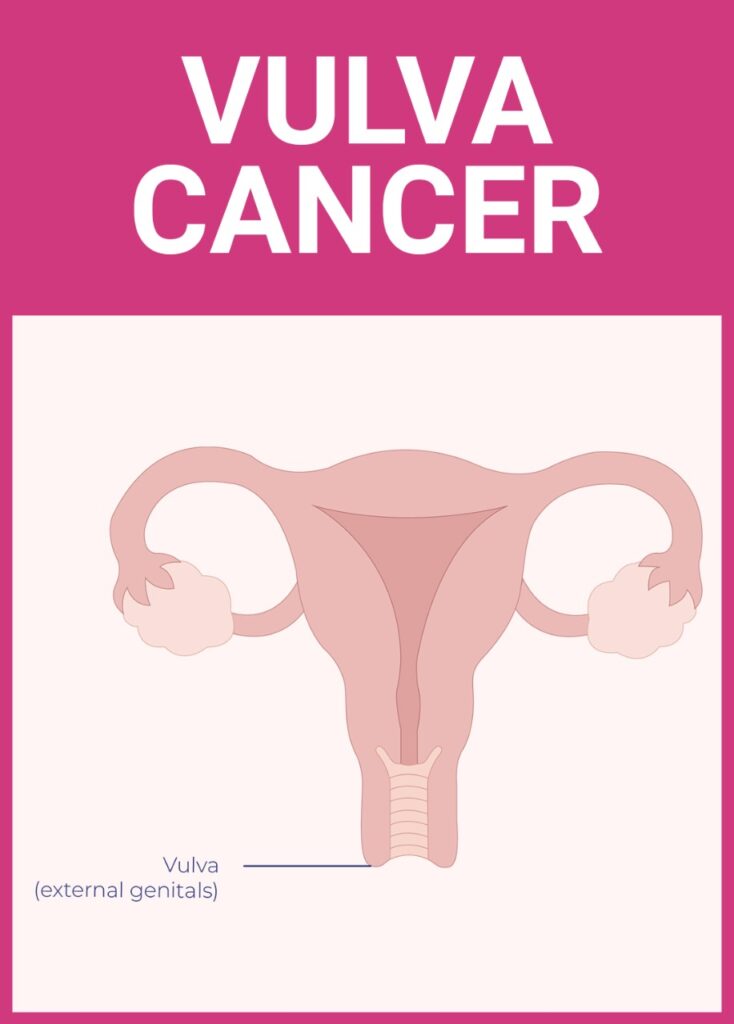
The vulva is the external part of the female genitals, including the clitoris, the vaginal lips, the opening to the vagina, and the surrounding skin and tissue. Most vulvar cancers are squamous cell carcinoma. This type of cancer begins in squamous cells (thin, flat skin cells) and is usually found on the vaginal lips. A small number of vulvar cancers are adenocarcinomas (cancers that begin in cells that make mucus and other fluids). This type of cancer is usually found on the sides of the vaginal opening.Vulvar cancer usually forms slowly over a number of years. Abnormal cells can grow on the surface of the vulvar skin for a long time. This condition is called vulvar intraepithelial neoplasia (VIN). Because it is possible for VIN to become vulvar cancer, it is important to get treatment.
These are common symptoms in women who have developed vulvar cancer.
- A lump or growth in or on the vulvar area
- A patch of skin that is differently textured or colored than the rest of the vulvar area
- Persistent itching, pain, soreness, or burning in the vulvar area
- Painful urination
- Bleeding or discharge that is not menstrual blood
- An ulcer that persists for more than 1 month
- A change in the appearance of an existing mole (this symptom is for vulvar melanoma specifically)
- Wart-like growths that are similar to genital warts
What are different vulvectomy approaches to treat invasive vulvar cancer ?
- Radical Local Excision of the Vulva:
- Modified Radical Vulvectomy
- Radical Vulvectomy
- Lymphadenectomy: this is a surgical procedure to remove lymph nodes in the groin in order to check for cancer
