What is Vaginal Cancer?
What is Vaginal Cancer?
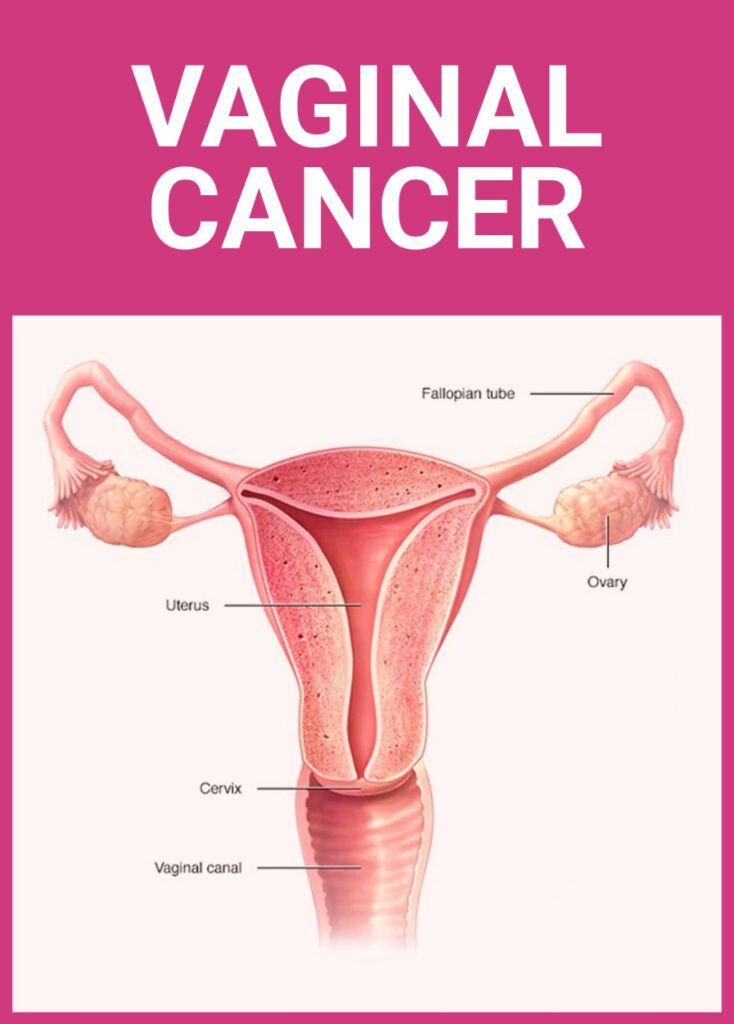
Vaginal cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the vagina. The vagina is the canal leading from the cervix (the opening of uterus) to the outside of the body. At birth, a baby passes out of the body through the vagina (also called the birth canal).Vaginal cancer is not common.
There Are Two Main Types Of Vaginal Cancer:
Squamous cell carcinoma: Cancer that forms in squamous cells, the thin, flat cells lining the vagina. Squamous cell vaginal cancer spreads slowly and usually stays near the vagina, but may spread to the lungs, liver, or bone. This is the most common type of vaginal cancer.
Adenocarcinoma: Cancer that begins in glandular (secretory) cells. Glandular cells in the lining of the vagina make and release fluids such as mucus. Adenocarcinoma is more likely than squamous cell cancer to spread to the lungs and lymph nodes.
What Are Are Common Risk Factor In Women Who Have Developed Vaginal Cancer?
Being aged 60 or older.
Being exposed to DES while in the mother’s womb. In the 1950s, the drug DES was given to some pregnant women to prevent miscarriage (premature birth of a fetus that cannot survive). Women who were exposed to DES before birth have an increased risk of vaginal cancer. Some of these women develop a rare form of vaginal cancer called clear cell adenocarcinoma.
- Having human papillomavirus (HPV) infection.
- Having a history of abnormal cells in the cervix or cervical cancer.
What is the treatment of Vaginal Cancer?
The treatment of vaginal cancer depends on the size and stage of tumor. It also depends on the location of the tumor in relation to urethra and anus. Surgery is done in early cases and for advanced stages patient gets radiation therapy.
